New Databricks INSERT Features: INSERT REPLACE ON and INSERT REPLACE USING
Databricks SQL continues to evolve with powerful new capabilities. Two exciting additions to the INSERT command are now available: INSERT REPLACE ON for replacing records that match specific conditions, and INSERT REPLACE USING for overwriting entire physical partitions. Let's explore these features in detail.
INSERT REPLACE ON: Conditional Record Replacement
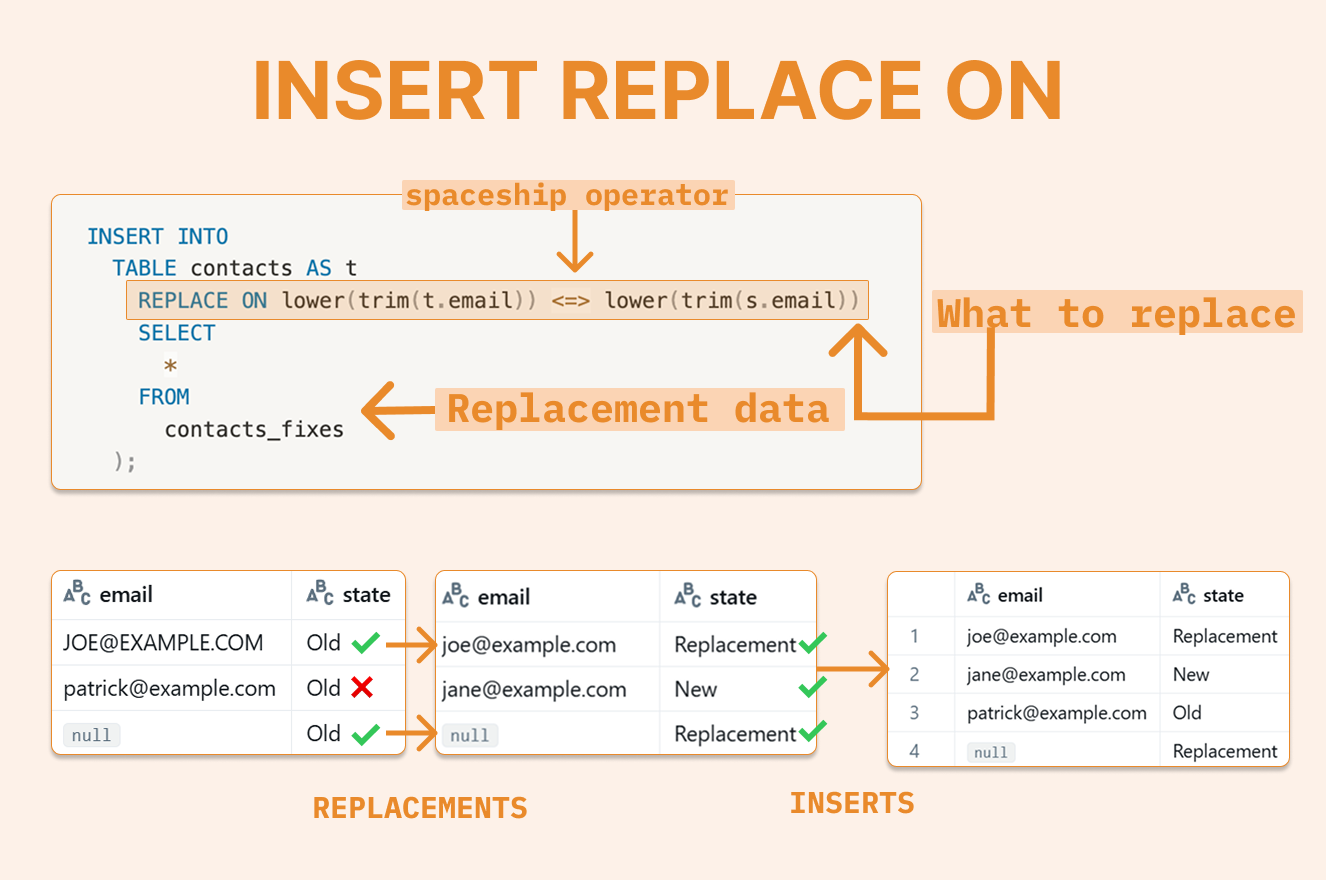
With INSERT REPLACE ON, you can specify a condition to target which rows should be replaced. The process works by first deleting all rows that match your expression (comparing source and target data), then inserting the new rows from your INSERT statement.
Use Case: Email Data Cleanup
Here's a practical example using the trim and lower functions with a condition to match and fix email addresses. We'll also use the <=> spaceship operator to safely handle NULL values, ensuring records with NULLs are properly caught and replaced.
This approach will:
Catch and replace
JOE@EXAMPLE.COMHandle NULL values (thanks to the
<=>operator)Insert
jane@example.comas a new record (wasn't in the target before)Leave
patrick@example.comunchanged (doesn't match the condition)
CREATE TABLE contacts(email STRING, state STRING);
INSERT INTO contacts
VALUES
('JOE@EXAMPLE.COM', 'Old'),
('patrick@example.com', 'Old'),
(NULL, 'Old');
CREATE TEMP VIEW contacts_fixes AS
SELECT
*
FROM
VALUES
('joe@example.com', 'Replacement'), -- will replace JOE@EXAMPLE.COM
('jane@example.com', 'New'), -- will be added as new record
(NULL, 'Replacement') -- will replace NULL using <=> operator safe for NULLs
AS s (email, state);
INSERT INTO
TABLE contacts AS t -- target table for replacement
REPLACE ON lower(trim(t.email)) <=> lower(trim(s.email)) ( -- <=> spaceship operator safe for NULL, functions allowed in expression
SELECT
*
FROM
contacts_fixes -- SELECT statement for replacement data
);
SELECT * FROM contacts;
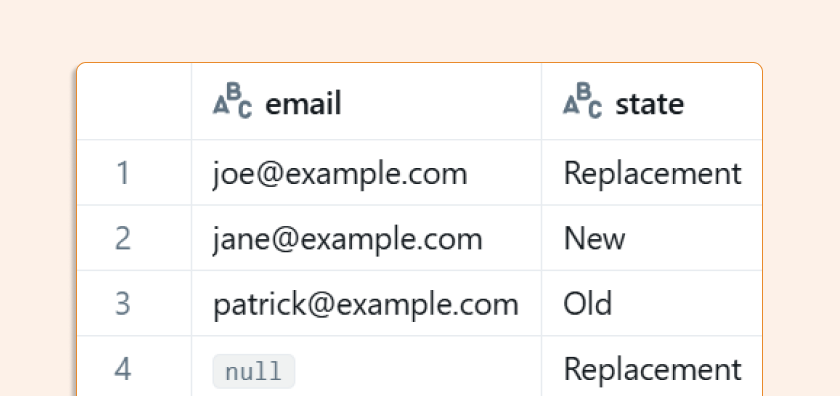
The results show that contacts matching the expression were successfully replaced:
REPLACE ON deletes records matching the condition and then inserts new ones. In the previous example, no deletions occurred, so let's look at a deletion scenario.
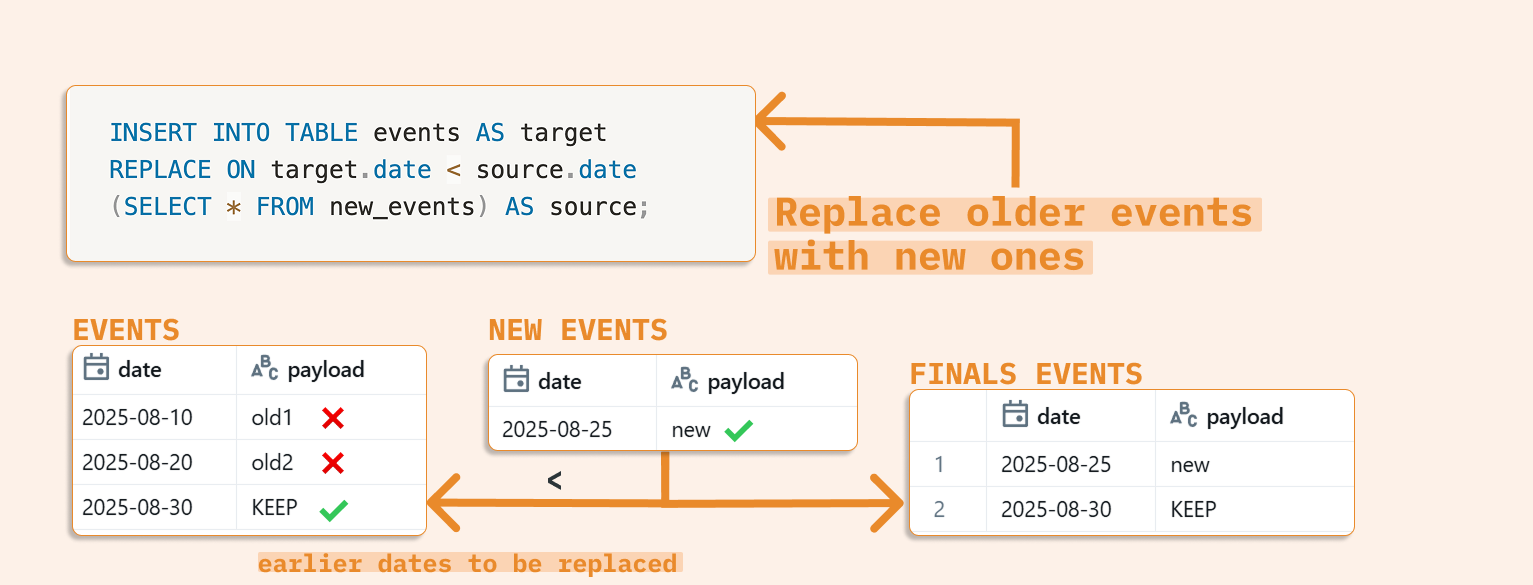
Use Case: Event Data Management
When new events arrive, you might want to delete all older events. Here's how to accomplish this with REPLACE ON:
CREATE TABLE events (date DATE, payload STRING); CREATE TABLE new_events (date DATE, payload STRING); INSERT INTO events VALUES (DATE'2025-08-10','old1'), (DATE'2025-08-20','old2'), (DATE'2025-08-30', 'KEEP'); -- marked as KEEP for demonstration - won't be deleted INSERT INTO new_events VALUES (DATE'2025-08-25', 'new'); -- inserting newer data; all older records will be deleted INSERT INTO TABLE events AS target REPLACE ON target.date < source.date (SELECT * FROM new_events) AS source; SELECT * FROM events ORDER BY date;
The results show that old1 and old2 were deleted because they were older than the new event date:
INSERT REPLACE USING: Partition-Level Replacement
In the past, partition overwrites were often handled in problematic ways, including operations outside of Delta Lake that caused integration issues with schema and history management.
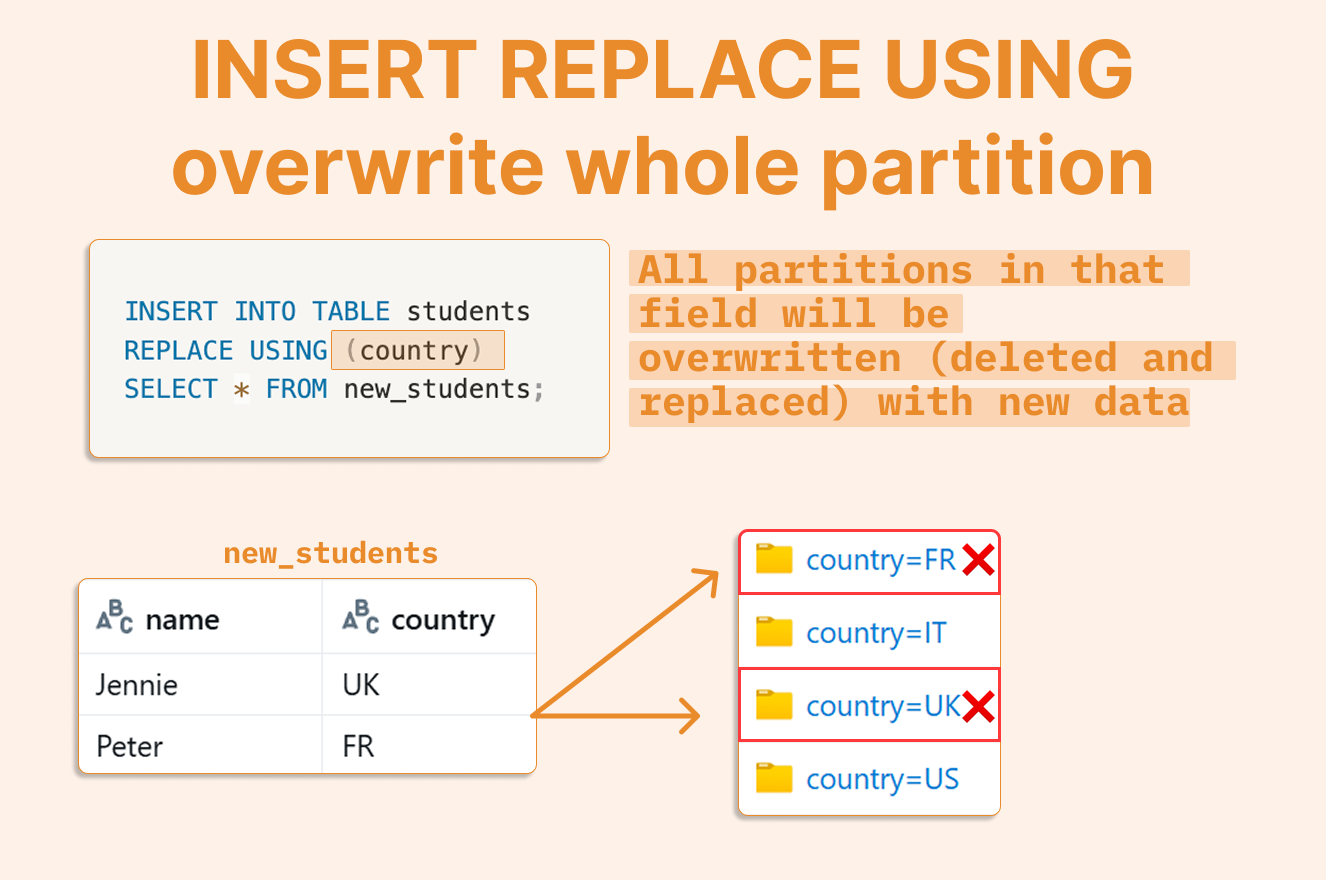
Now we have a best practice solution: INSERT REPLACE USING (field) ensures that partitions specified in the field are completely overwritten. The field values must correspond to the partitions you want to replace.
Since this performs folder-level overwrites, it applies to classic partitions, not liquid partitions.
Let's create a partitioned table to demonstrate:
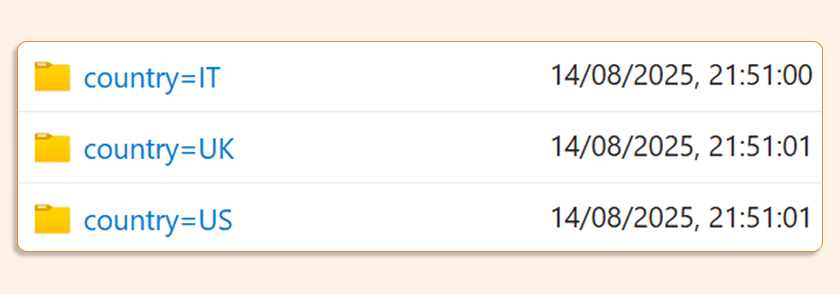
CREATE TABLE students (name STRING, country STRING)
PARTITIONED BY (country);
-- Insert initial data into US, UK, and IT partitions
INSERT INTO students VALUES
('Dylan', 'US'),
('Doug', 'UK'),
('Julia', 'IT');
You can see the partitioned structure in the storage account:
Now let's create a view with data that will replace entire partitions:
-- New data to replace the UK partition and add an FR partition
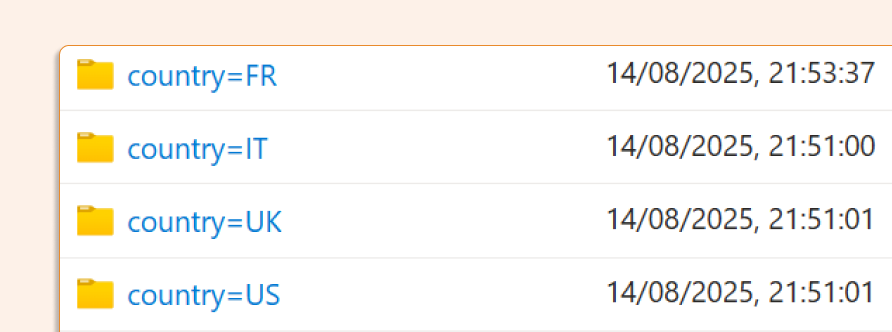
CREATE OR REPLACE TEMP VIEW new_students AS SELECT * FROM VALUES
('Jennie', 'UK'), -- will replace all data in the UK partition
('Peter', 'FR') AS s(name, country); -- will create a new FR partition
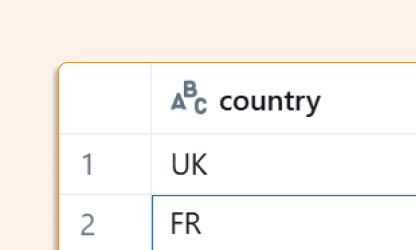
First, let's validate which partitions will be affected:
SELECT country FROM new_students;
Now perform the dynamic partition overwrite using the country key:
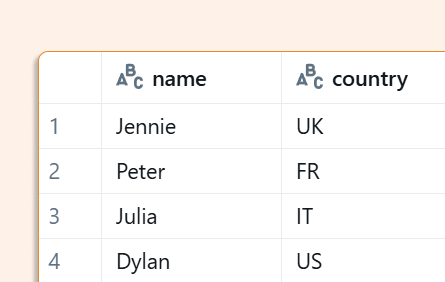
INSERT INTO TABLE students REPLACE USING (country) SELECT * FROM new_students;
Looking at the storage after the operation, we can see that the FR partition was created:
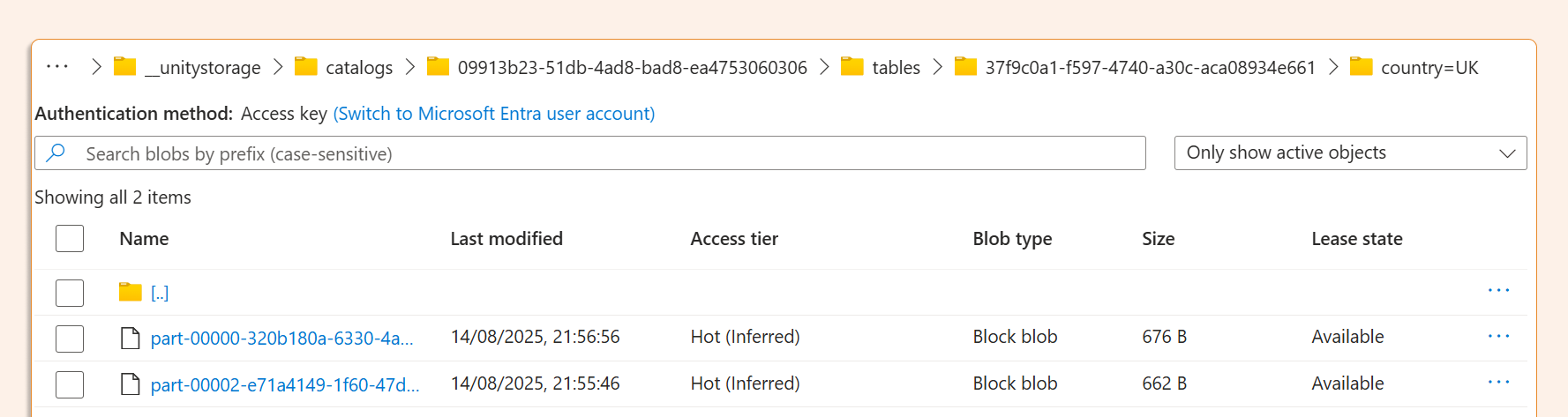
Examining the UK folder, we see a new parquet file that overwrites the old one. Since this is a Delta table and we maintain Delta history, the old parquet file remains alongside the new one:
Finally, let's verify the data shows the UK partition is overwritten, FR is added, and the rest remains unchanged:
Version Availability
INSERT REPLACE USING: Available in Databricks Runtime 16.3+
INSERT REPLACE ON: Available in Databricks Runtime 17.1+
These new INSERT features provide powerful, Delta-native ways to manage data updates and partition overwrites, eliminating the need for complex workarounds while maintaining data integrity and history.